New GST Rates Two-Slab Structure 2025!
On September 3-4, 2025 the 56th GST Council meeting, chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, announced a major overhaul of India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) system, effective from September 22, 2025. The key changes involve simplifying the existing four-tier GST slab structure (5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%) into a two-tier system with primary slabs of 5% and 18%, alongside a new 40% slab for luxury and sin goods. Below is a detailed summary of the GST slab changes and their implications, based on recent updates.
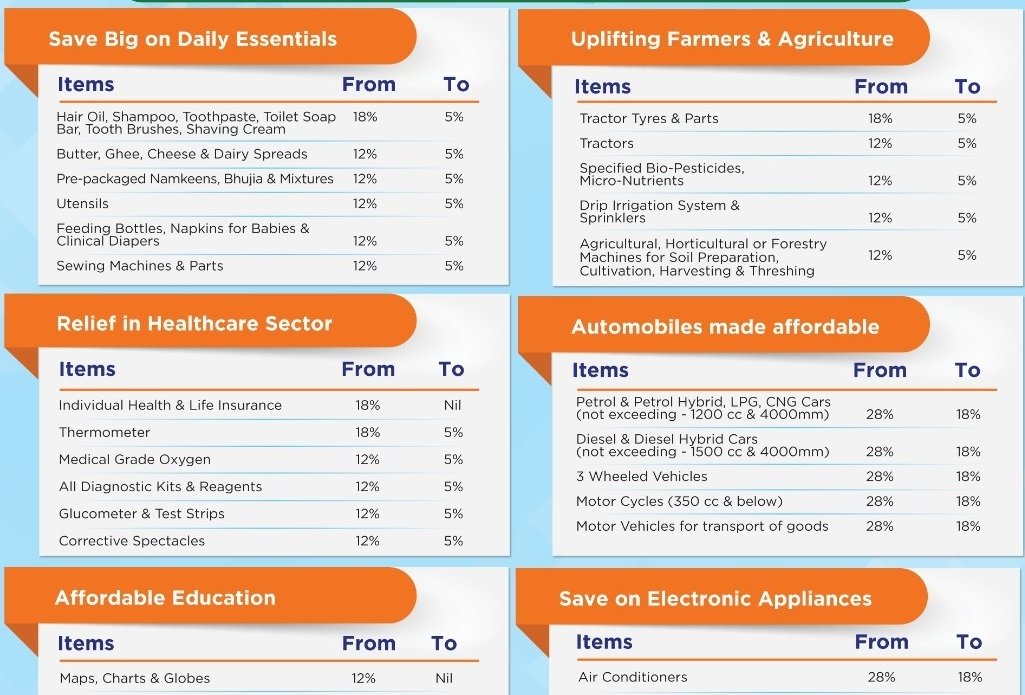
Key GST Slab Changes (Effective September 22, 2025):
Elimination of 12% and 28% Slabs:
- The 12% and 28% GST slabs have been abolished to simplify the tax structure.
- Approximately 99% of items previously under the 12% slab will move to the 5% slab, and 90% of items in the 28% slab will shift to the 18% slab.
- This aims to reduce tax disputes, ease compliance, and boost consumption by lowering the tax burden on consumers.
Two Main Slabs: 5% and 18%:
- 5% Slab: Includes daily essentials such as hair oil, toilet soap, shampoos, toothbrushes, toothpaste, bicycles, tableware, kitchenware, dry fruits, biscuits, ice cream, namkeen, corn flakes, butter, ghee, and packaged food.
- 18% Slab: Covers aspirational items like televisions (all sizes now taxed at 18%, down from 28% for TVs above 32 inches), air conditioners, dishwashing machines, motorcycles (up to 350 cc), small cars (up to 350 cc), buses, trucks, ambulances, and auto parts.
New Maruti Suzuki Celerio 2025
New 40% Slab for Luxury and Sin Goods:
- A new 40% GST slab has been introduced for sin goods (e.g., pan masala, tobacco, cigarettes, bidis, aerated water, carbonated/caffeinated beverages) and luxury items (e.g., motorcycles exceeding 350 cc, petrol cars above 1,200 cc, diesel cars above 1,500 cc, yachts, and helicopters).
- Tobacco products, cigarettes, and bidis will continue at the existing 28% GST rate plus compensation cess until loans related to the cess are repaid, with a transition to the 40% slab expected by 2028.
Exemptions and Reductions:
- Health and Insurance: Individual life and health insurance policies, including family floater plans, are now exempt from GST (previously 12%). Life-saving drugs, including anti-cancer medicines, and medical items like thermometers and glucometers will be taxed at 0% or 5%.
- Agriculture and Health: Farmers and the agriculture sector will benefit from lower rates on farm goods. Health-related items and services see significant tax relief.
- Fortified Rice Kernel (FRK): Now taxed at 5% under HSN 1904.
- Gene Therapy: Exempt from GST.
- Skill Training: Approved skill training partners of NSDC are now GST-exempt (previously 18%).
Inverted Duty Structure Corrections:
- Issues with inverted duty structures (where inputs are taxed higher than finished products) have been addressed. For example, man-made fibre and yarn have been reduced from 18% and 12% to 5%.
- This correction aims to free up working capital and enhance manufacturing competitiveness.
Implementation and Economic Impact:
- Effective Date: The new GST rates will take effect from September 22, 2025, coinciding with the start of Navratri, described as a “Diwali gift” for consumers.
- Revenue Implications: The government expects a short-term revenue loss of approximately ₹48,000 crore due to the rate cuts, but anticipates increased consumption, reduced tax evasion, and a wider tax base to offset this.
- Consumer Benefits: Lower taxes on essentials (e.g., toothpaste, shampoo, footwear below ₹1,000) and aspirational goods (e.g., TVs, small cars) are expected to increase disposable income, boost demand, and potentially reduce inflation.
- Business and MSME Support: Simplified slabs reduce classification disputes and compliance burdens. Automated refunds, pre-filled GST returns, and easier registration processes will support MSMEs and startups.
- Industry Impact: Sectors like FMCG, electronics, automotive, insurance, and hospitality are expected to see increased demand. For example, footwear brands like Bata have already announced price reductions to pass on the GST cut benefits.
Specific Examples of Rate Changes:
Cheaper Items (Moved to 0% or 5%):
- Food: UHT milk, paneer, Indian breads, dry fruits, butter, ghee, namkeen, biscuits, corn flakes.
- Household: Hair oil, soap, shampoo, toothpaste, toothbrushes, bicycles, tableware, kitchenware.
- Footwear: Footwear below ₹1,000 now at 5% (down from 12%).
Cheaper Items (Moved to 18%):
- Electronics: TVs (all sizes), air conditioners, dishwashers.
- Automotive: Small cars (up to 350 cc), buses, trucks, ambulances, auto parts, motorcycles up to 350 cc.
Costlier Items (Moved to 40%):
- Luxury vehicles: Petrol cars above 1,200 cc, diesel cars above 1,500 cc, motorcycles above 350 cc.
- Sin goods: Pan masala, tobacco, aerated beverages, online gaming (potentially reclassified as a demerit good).
- Unchanged (for now): Tobacco products, cigarettes, and bidis remain at 28% GST plus compensation cess until loans are cleared.
- Compensation Cess: The compensation cess regime, set to end by March 31, 2026, will no longer apply to most goods, except for tobacco-related products until loans are repaid. For example, coal’s compensation cess of ₹400/ton has been merged into the GST rate.









Leave a Reply